иҝ‘е№ҙгҖҒиҶңеҲҶйӣўжҠҖиЎ“гҒҜгҖҒдёӢж°ҙеҮҰзҗҶгҒ®ж–°жҠҖиЎ“гҒ®дёҖгҒӨгҒЁгҒ—гҒҰеәғгҒҸз ”з©¶гҒ•гӮҢгҖҒеҝңз”ЁгҒ•гӮҢгҒҰгҒ„гҒҫгҒҷгҖӮйҮҚеҠӣеҲҶйӣўгҖҒеҮқеӣәгҖҒгӮЁгғһгғ«гӮёгғ§гғіз ҙеЈҠгҖҒжІ№еҗёеҸҺгҒҠгӮҲгҒіи„ұи„ӮгҖҒз”ҹеҲҶи§ЈгҖҒеҮқйӣҶеҗёзқҖгҖҒгӮӨгӮӘгғідәӨжҸӣгҖҒгҒқгҒ®д»–гҒ®еҫ“жқҘгҒ®еҲҶйӣўгғ—гғӯгӮ»гӮ№гҒӘгҒ©гҒ®д»–гҒ®жҠҖиЎ“гҒЁжҜ”ијғгҒ—гҒҰгҖҒгҒ“гҒ®жҠҖиЎ“гҒ«гҒҜеӨҡгҒҸгҒ®еҲ©зӮ№гҒҢгҒӮгӮҠгҒҫгҒҷгҖӮдҫӢгҒҲгҒ°гҖҒйҒёжҠһжҖ§гҒҢеј·гҒҸгҖҒгӮЁгғҚгғ«гӮ®гғјж¶ҲиІ»йҮҸгҒҢе°‘гҒӘгҒҸгҖҒйҒ©з”ЁзҜ„еӣІгҒҢеәғгҒҸгҖҒз’°еўғгҒ«е„ӘгҒ—гҒҸгҖҒиЁӯеӮҷгҒҢз°ЎеҚҳгҒ§гҖҒж“ҚдҪңгҒҢз°ЎеҚҳгҒӘгҒ©гҒ§гҒҷгҖӮжІ№ж°ҙеҲҶйӣўиҶңгҒҜгҖҒжқҗиіӘгҒ«гӮҲгҒЈгҒҰжңүж©ҹиҶңгҒЁз„Ўж©ҹиҶңгҒ«еҲҶгҒ‘гӮүгӮҢгҒҫгҒҷгҖӮжңүж©ҹиҶңгҒҜгҖҒ科еӯҰз ”з©¶гӮ„е•ҶжҘӯеҲҶйҮҺгҒ§е№…еәғгҒ„з”ЁйҖ”гҒҢгҒӮгӮҠгҒҫгҒҷгҖӮжңүж©ҹиҶңгҒЁжҜ”ијғгҒ—гҒҰгҖҒз„Ўж©ҹгӮ»гғ©гғҹгғғгӮҜиҶңгҒҜеҢ–еӯҰзҡ„гҒҠгӮҲгҒізҶұзҡ„е®үе®ҡжҖ§гҒҢеј·гҒҸгҖҒжұҡгӮҢгҒ«еҜҫгҒҷгӮӢиҖҗжҖ§гҒЁиҖҗең§жҖ§гҒ«е„ӘгӮҢгҖҒжё…жҺғгҒҢе®№жҳ“гҒ§гҖҒж©ҹжў°зҡ„еј·еәҰгҒҢй«ҳгҒҸгҖҒеҜҝе‘ҪгҒҢй•·гҒ„гҒҹгӮҒгҖҒжІ№дёӯж°ҙгӮЁгғһгғ«гӮёгғ§гғіеҲҶйӣўгҒ«гӮ»гғ©гғҹгғғгӮҜиҶңгӮ’дҪҝз”ЁгҒҷгӮӢгҒ“гҒЁгҒҜеӨ§гҒҚгҒӘгғҲгғ¬гғігғүгҒ§гҒҷгҖӮз–Һж°ҙжҖ§ж”№иіӘгҒ«гӮҲгӮҠгҖҒгӮ»гғ©гғҹгғғгӮҜиҶңгҒ®жІ№гҒ«еҜҫгҒҷгӮӢжҝЎгӮҢжҖ§гҒҢеҗ‘дёҠгҒ—гҖҒжІ№дёӯж°ҙгӮЁгғһгғ«гӮёгғ§гғігҒ®еҲҶйӣўеҠ№зҺҮгҒҢеҗ‘дёҠгҒ—гҖҒгӮ»гғ©гғҹгғғгӮҜиҶңгҒ®еҢ–еӯҰзҡ„е®үе®ҡжҖ§гҒЁиҖҗд№…жҖ§гҒҢеҗ‘дёҠгҒ—гҒҫгҒҷгҖӮ
жІ№дёӯж°ҙпјҲW/OпјүгӮЁгғһгғ«гӮёгғ§гғігӮ·гӮ№гғҶгғ гҒ®еҪўж…ӢгҒҜгҖҒж°ҙгҒҢе°ҸгҒ•гҒӘж¶Іж»ҙгҒ®еҪўгҒ§жІ№гҒ«еҲҶж•ЈгҒ—гҒҰгҒ„гӮӢгҒ“гҒЁгҒ§гҒҷгҖӮиҶңеҲҶйӣўдёӯгҒ®иҶңжұҡжҹ“гҒҜгҖҒдҪҝз”ЁжҷӮй–“гҒ®е»¶й•·гҒЁгҒЁгӮӮгҒ«йҖҸйҒҺжөҒжқҹгҒЁдҝқжҢҒзҺҮгҒ®дҪҺдёӢгӮ’жӢӣгҒҚгҖҒиҶңгҒ®иҖҗз”Ёе№ҙж•°гӮ’зҹӯзё®гҒ—гҖҒиҶңеҲҶйӣўжҠҖиЎ“гҒ®еҝңз”ЁгӮ’еҲ¶йҷҗгҒ—гҒҫгҒҷгҖӮгӮ»гғ©гғҹгғғгӮҜиҶңиЎЁйқўгҒ®ж”№иіӘгҒ«гӮҲгӮҠгҖҒиҶңгҒ®зү№е®ҡгҒ®йҒёжҠһжҖ§гҒЁеҲҶйӣўеҠ№жһңгҒҢеҗ‘дёҠгҒ—гҖҒиҶңиЎЁйқўгҒЁдёҚиҰҒгҒӘдҫӣзөҰеҲҶеӯҗгҒЁгҒ®зӣёдә’дҪңз”ЁгҒҢжёӣе°‘гҒ—гҖҒиҶңжұҡжҹ“гҒҢгҒӮгӮӢзЁӢеәҰи»ҪжёӣгҒ•гӮҢгҒҫгҒҷгҖӮгҒ—гҒҹгҒҢгҒЈгҒҰгҖҒжІ№дёӯж°ҙгӮЁгғһгғ«гӮёгғ§гғігҒ®еҲҶйӣўгҒ§гҒҜйҖҡеёёгҖҒз–Һж°ҙжҖ§гғ•гӮЈгғ«гғ гҒҢйҒёжҠһгҒ•гӮҢгҒҫгҒҷгҖӮгҒ“гӮҢгҒ«гӮҲгӮҠгҖҒиҶңиЎЁйқўгҒ®з–Һж°ҙжҖ§гҒЁиҰӘжІ№жҖ§гҒ®зү№жҖ§гӮ’еҲ©з”ЁгҒ—гҒҰгҖҒжІ№ж»ҙгҒҜйҖҡйҒҺгҒ—гҖҒж°ҙж»ҙгҒҜжҚ•жҚүгҒ•гӮҢгҖҒжІ№ж°ҙеҲҶйӣўгҒ®еҠ№жһңгҒҢеҫ—гӮүгӮҢгҒҫгҒҷгҖӮ
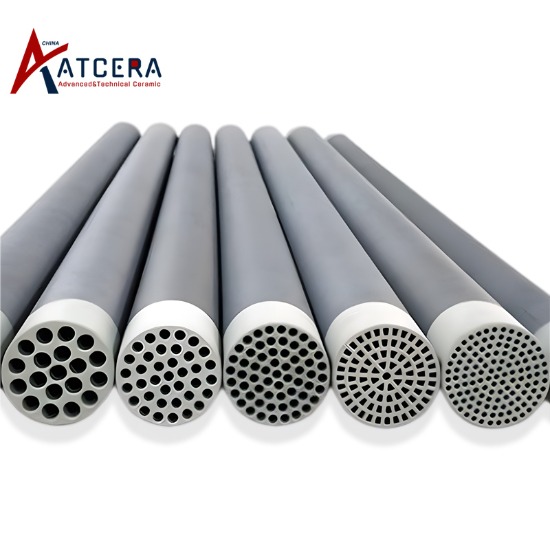

гӮ»гғ©гғҹгғғгӮҜиҶңиЎЁйқўгҒ®з–Һж°ҙжҖ§ж”№иіӘ
гӮ»гғ©гғҹгғғгӮҜгғ•гӮЈгғ«гғ иЎЁйқўгҒ®з–Һж°ҙжҖ§ж”№иіӘгҒҜгҖҒйҖҡеёёгҖҒз–Һж°ҙжҖ§жқҗж–ҷгӮ’зө„гҒҝеҗҲгӮҸгҒӣгҒҹгӮҠжҺҘзқҖгҒ—гҒҹгӮҠгҖҒгӮҲгӮҠдҪҺгҒ„иЎЁйқўгӮЁгғҚгғ«гӮ®гғјгҖҒйҒ©еҲҮгҒӘзІ—гҒ•гҒҠгӮҲгҒіиЎЁйқўж§ӢйҖ гӮ’йҒёжҠһгҒ—гҒҹгӮҠгҒҷгӮӢгҒ“гҒЁгҒ§е®ҹзҸҫгҒ•гӮҢгҒҫгҒҷгҖӮгҒҹгҒЁгҒҲгҒ°гҖҒгӮ·гғ©гғігҒҫгҒҹгҒҜгғҒгӮӘгғјгғ«гӮ’дҪҝз”ЁгҒ—гҒҰиЎЁйқўгҒ®еҢ–еӯҰзү№жҖ§гӮ’д»ҳдёҺгҒ—гҒҹгӮҠгҖҒгғҹгӮҜгғӯгғігҒҫгҒҹгҒҜгғҠгғҺж§ӢйҖ гӮ’е°Һе…ҘгҒ—гҒҰгӮҲгӮҠзІ—гҒ„иЎЁйқўгӮ’еҫ—гҒҹгӮҠгҖҒгғ•гӮЈгғ«гғ иЎЁйқўгҒ®з–Һж°ҙеҠ№жһңгӮ’ж”№е–„гҒ—гҒҰеҲҶйӣўжҖ§иғҪгӮ’й«ҳгӮҒгҒҹгӮҠгҒ—гҒҫгҒҷгҖӮ
гӮ»гғ©гғҹгғғгӮҜиҶңиЎЁйқўгҒ®з–Һж°ҙжҖ§ж”№иіӘгҒ«гҒҜгҖҒеҗ«жөёжі•гҖҒгӮҫгғ«гӮІгғ«жі•гҖҒеҢ–еӯҰи’ёзқҖжі•гҒ® 3 гҒӨгҒ®дёҖиҲ¬зҡ„гҒӘж–№жі•гҒҢгҒӮгӮҠгҒҫгҒҷгҖӮ
01. гғҮгӮЈгғғгғ—жі•
Impregnation method (Impregnation method) does not require special equipment, just the original ceramic film directly immersed in hydrophobic substance solution, the method is simple and direct, easy to operate, low cost. The hydrophobic modification of ceramic membrane surface is carried out by immersion method, which usually uses the functional group of hydrophobic substance to connect with the hydroxyl group on the ceramic membrane surface through condensation reaction.
Taking siloxane as a modifier for example, the operation steps of the impregnation method are as follows: dissolve the organosilane in water or ethanol and hydrolyze it to obtain a reactive silanol solution; When the pre-treated ceramic membrane is immersed in the solution, the reactive silane molecules can be adsorbed on the surface of the membrane, and the hydrophobic membrane can be obtained.
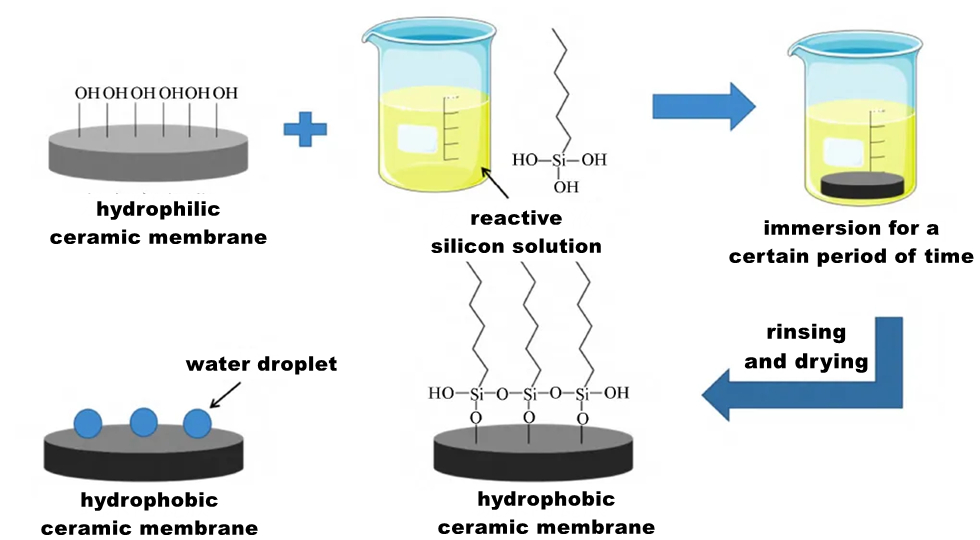
Hydrophobic effect is the result of the joint action of surface roughness and surface energy. In the study of hydrophobic modification of ceramic film, it is usually first to provide a certain rough micro-nano structure on the surface of ceramic film, and then modify it with low surface energy. In addition to the modification with silane coupling agent, mercaptan is also the preferred material to reduce the surface energy of the film.
In summary, the operation and steps of hydrophobic modification of the surface of ceramic film by impregnation method are relatively simple, and are greatly affected by the type of modifier, the concentration of modifier, the impregnation time, the number of impregnation times and the roughness of the surface of ceramic film. In addition, because the number of substances with low surface energy that react depends on its own concentration and the number of hydroxyl groups on the surface of ceramic film, Therefore, the method also has a great dependence on the reactive hydroxyl group on the surface of the ceramic membrane.
02. Sol-gel method
Sol-gel technique uses compounds containing highly chemically active components as precursors, and mixes these raw materials uniformly in the liquid phase. After chemical reactions such as hydrolysis and condensation, a stable transparent Sol system is formed in the solution. The sol is slowly polymerized among aged colloidal particles to form a gel with a three-dimensional network structure. The gel was dried and sintered to produce molecular and even nanostructured materials.
The hydrophobic modification of ceramic membrane by sol-gel method can form a large rough structure on the surface of the membrane, and can directly bind low surface energy chemicals. However, the early introduction of organosilane into the sol solution may lead to the formation of large volume polymers, resulting in poor modification effects.
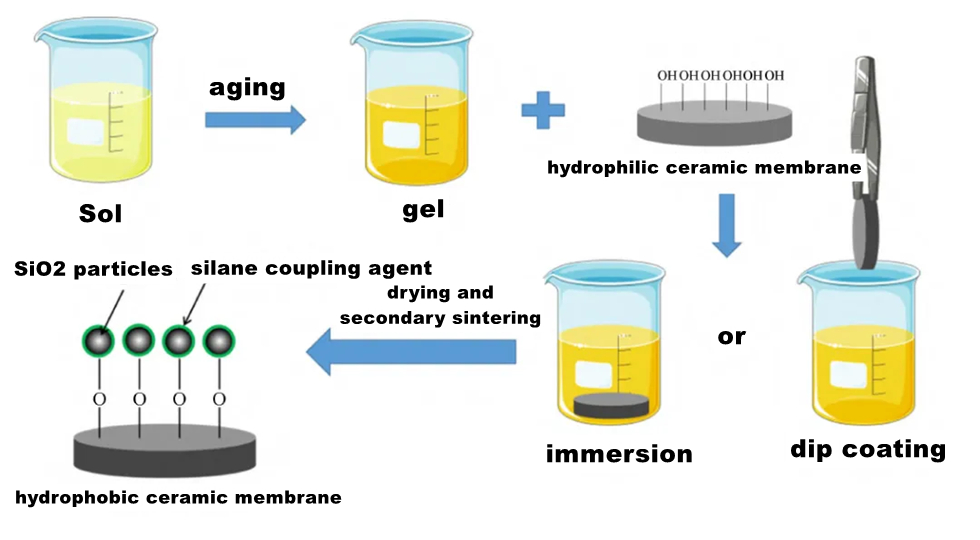
Compared with other methods, sol-gel method can prepare a stable hydrophobic surface with good separation effect, but it takes a long time to prepare the sol solution, and macromolecular polymers may be formed in the process, which affects the modification effect. In general, secondary sintering is required after the completion of coating, and the process is more complicated. In addition, excessive temperature during secondary sintering will destroy the structure of the film, reduce the hydrophobicity and stability of the film, and the aperture of the modified film will decrease with the increase of the number and time of sol-gel coating. In addition, the sol has an important effect on the formation of colloid in the process of colloid preparation, and then affects the film forming quality. Coating time and times, ambient temperature and humidity, heating rate, calcination temperature and calcination time all have a great influence on the subsequent coating drying process. At present, the process can be simplified by reducing the sintering steps at high temperature, forming a rough structure on the surface of the film at one time and combining with low surface energy materials, so as to reduce the damage of the film structure at high temperature.

03 Chemical vapor deposition method
chemical vapor deposition (CVD) uses gas phase reactants deposited on the substrate surface to form a solid film with specific chemical properties. The method has the advantages of controllable film composition, good film repeatability, uniform film layer, wide application range, no restriction on the shape of the substrate and no damage to the substrate material, and is an effective method to change the surface properties and microstructure of the film. For hydrophobic modification of the ceramic film using this method, the ceramic film needs to be placed in a closed container and heated at the boiling point temperature of the organosilane for a long time. The organosilane vapor is passed through to react with the hydroxyl group on the surface of the ceramic film, and the reaction principle is the same as that of the impregnation method.
Under normal circumstances, in order to make the organosilane reagent can be fully utilized, it is necessary to select a closed container with a size similar to the ceramic membrane, so that the contact and reaction of organosilane vapor with the ceramic membrane can be maximized.
еҢ–еӯҰи’ёзқҖпјҲCVDпјүгҒҜгҖҒи–„иҶңиЎЁйқўгҒ«гғһгӮӨгӮҜгғӯгғҠгғҺзІ’еӯҗгӮ„гғҠгғҺгғӯгғғгғүгӮ’дҪңиЈҪгҒ—гҖҒ秩еәҸгҒ гҒЈгҒҹеҫ®зҙ°ж§ӢйҖ гӮ’еҪўжҲҗгҒҷгӮӢгҒҹгӮҒгҒ®еҘҪгҒҫгҒ—гҒ„ж–№жі•гҒ§гҒҷгҖӮеҢ–еӯҰи’ёзқҖжі•гҒ§ж”№иіӘгҒ—гҒҹз–Һж°ҙжҖ§гӮ»гғ©гғҹгғғгӮҜи–„иҶңгҒҜгҖҒи–„иҶңеұӨгҒҢеқҮдёҖгҒ§гҖҒе®үе®ҡжҖ§гҒҢиүҜеҘҪгҒ§гҖҒеҝңз”ЁзҜ„еӣІгҒҢеәғгҒ„гҒӘгҒ©гҒ®еҲ©зӮ№гҒҢгҒӮгӮҠгҒҫгҒҷгҒҢгҖҒеҗҢжҷӮгҒ«гҖҒз–Һж°ҙжҖ§и–„иҶңгҒ®еҺҡгҒ•гҒҢи–„гҒҸгҖҒж©ҹжў°зҡ„жҖ§иіӘгҒҢдёҚеҚҒеҲҶгҒ§гҖҒеӨ–йғЁиЎқж’ғгҒ«гӮҲгӮҠдәҖиЈӮгӮ„ж°—жіЎгҒӘгҒ©гҒ®ж¬ йҷҘгҒҢзҷәз”ҹгҒ—гӮ„гҒҷгҒ„гҒЁгҒ„гҒҶж¬ зӮ№гҒҢгҒӮгӮҠгҒҫгҒҷгҖӮж°ҙж»ҙгӮ„жұҡжҹ“зү©иіӘгҒҢдәҖиЈӮгҒӢгӮүи–„иҶңгҒ«жөёйҖҸгҒ—гҖҒи–„иҶңгҒ®еҶ…йғЁж§ӢйҖ гӮ’з ҙеЈҠгҒ—гҖҒи–„иҶңгҒ®з–Һж°ҙжҖ§гҒЁе®үе®ҡжҖ§гӮ’дҪҺдёӢгҒ•гҒӣгҒҫгҒҷгҖӮе Ҷз©ҚеҸҚеҝңгҒ«й–ўдёҺгҒҷгӮӢжңүж©ҹгӮ·гғ©гғігҒ®дёӯгҒ«гҒҜжҜ’жҖ§гҒ®гҒӮгӮӢгӮӮгҒ®гӮӮгҒӮгӮҠгҖҒдәәдҪ“гӮ„з’°еўғгҒ«е®ігӮ’еҸҠгҒјгҒ—гҒҫгҒҷгҖӮгҒҫгҒҹгҖҒгҒ“гҒ®ж–№жі•гҒ§гҒҜеҸҚеҝңжё©еәҰгҒҢй«ҳгҒҸгҖҒгҒқгӮҢгҒ«дјҙгҒҶй«ҳгӮЁгғҚгғ«гӮ®гғјж¶ҲиІ»гҒЁй«ҳгӮігӮ№гғҲгҒ«гӮҲгӮҠгҖҒе®ҹйҡӣгҒ®е·ҘжҘӯз”ҹз”ЈгҒёгҒ®еҝңз”ЁгҒҢеҲ¶йҷҗгҒ•гӮҢгҒҫгҒҷгҖӮ





























